CodeIgniter Hooks allows you to execute a script with specific path within the CodeIgniter execution process without updating or modifying the core files. If you need to execute a code that should run every time after constructor of a controller is loaded, you specify that script path in hooks.
CodeIgniter's Hooks feature provides a means to tap into and modify the inner workings of the framework without hacking the core files.
Enabling Hooks
The hooks feature can be globally enabled/disabled by setting the following item in the application/config/config.php file.
$config['enable_hooks'] = TRUE;
Defining a Hook
Hooks are defined in the application/config/hooks.php file. Each hook is specified as an array with this prototype:
$hook['pre_controller'] = array(
'class' => 'MyClass',
'function' => 'Myfunction',
'filename' => 'Myclass.php',
'filepath' => 'hooks',
'params' => array('element1', 'element2', 'element3')
);
Multiple calls to the same Hook
You can use multi-dimensional array to use the same hook point with more than one script, like this:
$hook['pre_controller'][] = array(
'class' => 'MyClass',
'function' => 'Myfunction',
'filename' => 'Myclass.php',
'filepath' => 'hooks',
'params' => array('element1', 'element2', 'element3')
);
$hook['pre_controller'][] = array(
'class' => 'MyClass2',
'function' => 'Myfunction2',
'filename' => 'Myclass2.php',
'filepath' => 'hooks',
'params' => array('element4', 'element5', 'element6')
);
Note: Brackets [] after each array index:
Hook Points
The following is a list of available hook points.
- pre_system Called very early during system execution. Only the benchmark and hooks class have been loaded at this point. No routing or other processes have happened.
- pre_controller Called immediately prior to any of your controllers being called. All base classes, routing, and security checks have been done.
- post_controller_constructor Called immediately after your controller is instantiated, but prior to any method calls happening.
- post_controller Called immediately after your controller is fully executed.
- display_override Overrides the
_display() method, used to send the finalized page to the web browser at the end of system execution. This permits you to use your own display methodology. Note that you will need to reference the CI superobject with $this->CI =& get_instance() and then the finalized data will be available by calling $this->CI->output->get_output().
- cache_override Enables you to call your own method instead of the
_display_cache() method in the Output Library. This permits you to use your own cache display mechanism.
- post_system Called after the final rendered page is sent to the browser, at the end of system execution after the finalized data is sent to the browser.
Hook Example
Using a text editor, create a controller called Site.php. In it, place this code and save it to your application/controllers/ directory:
<?php
class Site extends CI_Controller {
public function index() {
echo " is Great !";
}
}
?>
Using a text editor, create a controller called myhook.php. In it, place this code and save it to your application/hooks/ directory:
<?php
class Myhook extends CI_Controller {
public function index() {
echo "Welcome to Nexladder, India";
}
}
?>
We need to define the hooks in the application/config/hooks directory:
$hook['pre_controller'] = array(
'class' => 'Myhook',
'function' => 'index',
'filename' => 'Myhook.php',
'filepath' => 'hooks',
'params' => array()
);
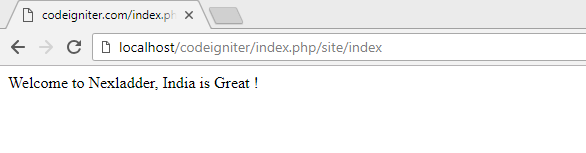
To try your form, visit your site using a URL similar to this one:
http://localhost/codeigniter/index.php/site/index
It will produce the following screen: